By comparing the fixed asset turnover ratio with other financial metrics, you can gain a more complete understanding of your company’s financial performance and identify areas for improvement. The fixed asset turnover ratio is a key indicator of a company’s ability to manage its assets and generate profit. Essentially, the higher the ratio, the more efficient a company is at using its fixed assets to produce revenue. It measures the effectiveness of a company’s fixed assets in generating sales and is often used by investors and financial analysts as a measure of a company’s operational efficiency. The fixed asset turnover ratio measures a company’s efficiency and evaluates it as a return on its investment in fixed assets such as property, plants, and equipment. In other words, it assesses the ability of a company to generate net sales from its machines and equipment efficiently.
- Conversely, if the value is on the other side, it indicates that the assets are not worth the investment.
- The type of industry a company operates in affects its asset turnover ratio.
- One critical consideration when evaluating the ratio is how capital-intensive the industry that the company operates in is (i.e., asset-heavy or asset-lite).
- A company can still have high costs that will make it unprofitable even when its operations are efficient.
- It varies significantly; capital-intensive industries usually have lower ratios, while service-oriented industries typically have higher ratios due to lower fixed asset investments.
- Since the total asset turnover consists of average assets and revenue, both of which cannot be negative, it is impossible for the total asset turnover to be negative.
Importance of the Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio for Your Business
Outsourcing some resources is the easiest way of decreasing fixed assets without limiting the company’s potential. For example, an e-commerce company may use a fulfillment service (link) instead of its warehouse. GOBankingRates works with many financial advertisers to showcase their products and services to our audiences. These brands compensate us to advertise their products in ads across our site. We are not a comparison-tool and these offers do not represent all available deposit, investment, loan or credit products. Balancing the assets your company owns and the liabilities you incur is important to do.
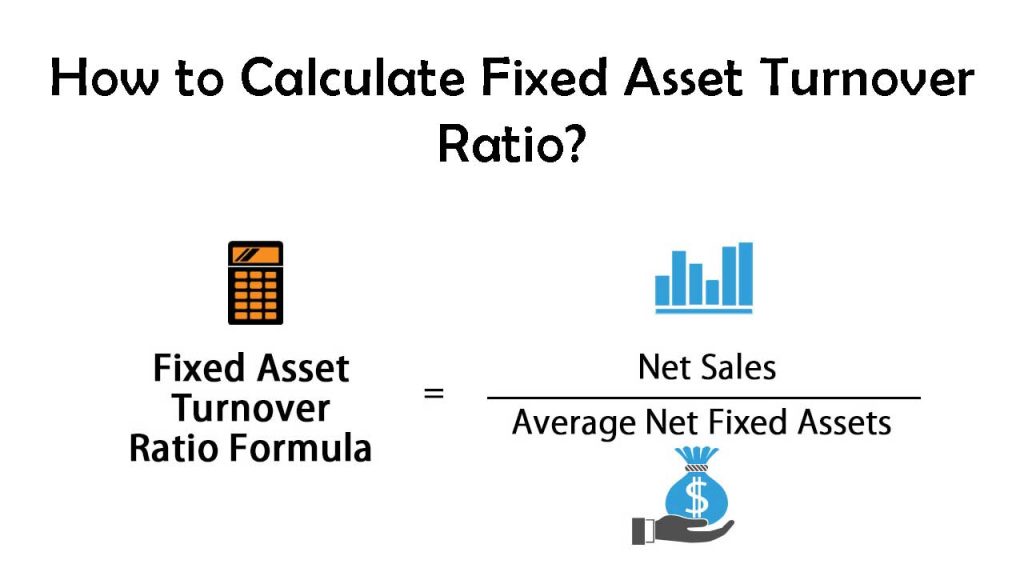
What Is Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio Formula?
For every dollar in assets, Walmart generated $2.51 in sales, while Target generated $1.98. Target’s turnover could indicate that the retail company was experiencing sluggish sales or holding obsolete inventory. Fixed assets such as property or equipment could be sitting idle or not being utilized to their full capacity. Fixed Asset Turnover is a widely used financial ratio; however, like all financial metrics, it comes with its set of limitations, which investors and analysts must consider for a comprehensive analysis. As we mentioned before, you should seek to increase the FAT ratio because a high value would mean you use your fixed assets efficiently. With our online FAT Ratio calculator, you can examine the operational efficiency of any company by analyzing how well a company utilizes its fixed asset to generate revenue.
How does Fixed Asset Turnover vary between industries?
The fixed asset turnover ratio formula measures the company’s ability to generate sales using fixed assets investments. One may calculate it by dividing the net sales by the average fixed assets. In conclusion, the fixed asset turnover ratio is an important metric to understand in order to assess your company’s operational efficiency and maximize your return on investment in fixed assets. By monitoring changes in this ratio and implementing appropriate strategies, you can make informed decisions that position your company for long-term success. The fixed asset turnover ratio can be a valuable tool in decision-making across various aspects of your business.
A high asset turnover ratio indicates effective asset utilization, which often translates to higher profitability. Conversely, a low ratio may signal inefficiencies or the need for strategic changes. However, it’s important to consider industry norms when evaluating this ratio, as asset utilization varies significantly across sectors. By using this ratio, companies can evaluate their productivity in using assets that are on hand. One way to measure this metric is to understand a business’s asset turnover ratio. Learn more about what exactly an asset turnover ratio is and how it’s calculated.
Understanding Asset Turnover Calculation
The asset turnover ratio considers the average total assets in the denominator, while the fixed asset turnover ratio looks at only fixed assets. The fixed asset turnover ratio (FAT ratio) is used by analysts to measure operating performance. The fixed asset turnover ratio is an important financial metric that helps companies assess their efficiency in using their fixed assets to generate sales. This ratio measures the amount of revenue a company is generating through the use of its fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, relative to the cost of those assets.
Interpreting the results of the fixed asset turnover ratio can provide insight into your company’s operational efficiency and profitability. A high ratio indicates that your company is generating significant revenue from its investment in fixed assets, whereas a low ratio may suggest inefficiencies in your operations. It is important to note, however, that the ideal ratio can vary by industry and the nature of your business. Thus, it helps to assess how well the company’s long term investments are able to bring adequate returns for the business.
It would not make sense to compare the asset turnover ratios for Walmart and AT&T, since they operate in different industries. Comparing the relative asset turnover ratios for AT&T with Verizon may provide a better estimate of which company is using assets more efficiently in that sector. The asset turnover ratio is used to evaluate how efficiently a company is using its assets to drive sales. It can be used to compare how a company is performing compared to its competitors, the rest of the industry, or its past performance. Additionally, the ratio doesn’t provide insights into the profitability or efficiency of individual assets within the company. Therefore, the ratio fails to tell analysts whether a company is profitable.
As a rule of thumb, however, a ratio of one or higher is generally considered acceptable, while ratios below one may signal inefficiencies in the use of fixed assets. However, it is important to note that irs form 1040 a high fixed asset turnover ratio may not always be a positive sign. It could indicate that the company is relying too heavily on its fixed assets and may not be investing enough in growth and innovation.
When interpreting a fixed asset figure, you must consider the manufacturing industry average. This will give you a better idea of whether a company’s ratio is bad or good. A company with a higher FAT ratio may be able to generate more sales with the same amount of fixed assets. A low turn over, on the other hand, indicates that the company isn’t using its assets to their fullest extent. Also, they might have overestimated the demand for their product and overinvested in machines to produce the products. It might also be low because of manufacturing problems like a bottleneck in the value chain that held up production during the year and resulted in fewer than anticipated sales.






