
Likewise, the $50,000 balance of labor cost that includes both direct labor and indirect labor will become zero after the journal entry. In accounting, labor cost journal entry will start with the period-end adjusting entry when the company needs to accrue the wages payable for the period. Later on, the company will need to assign the labor cost to appropriate manufacturing accounts. A company operates a factory which employed 40 direct workersthroughout the four-week period just ended. Direct employees were paidat a basic rate of $4.00 per hour for a 38-hour week. Overtime, which ispaid at a premium of 35%, is worked in order to meet general productionrequirements.
Conceptual Journey of Inventory & Wages Across Financial Statements
Examples includehome builders who design specific houses for each customer andaccumulate the costs separately for each job, and caterers whoaccumulate the costs of each banquet separately. Consulting, law,and public accounting firms use job costing to measure the costs ofserving each client. Motion pictures, printing, and otherindustries where unique jobs are produced use job costing.Hospitals also use job costing online bookkeeping services for small businesses bench accounting to determine the cost of eachpatient’s care. It is essential that organisations employ relevant methods in bothmanufacturing and service industries to relate the labour costs incurredto the work done. One of the ways in which this can be done is to makerecords of the time spent by employees doing jobs. These are overheads that the company incurs, and therefore, they can be referred to as fixed costs.
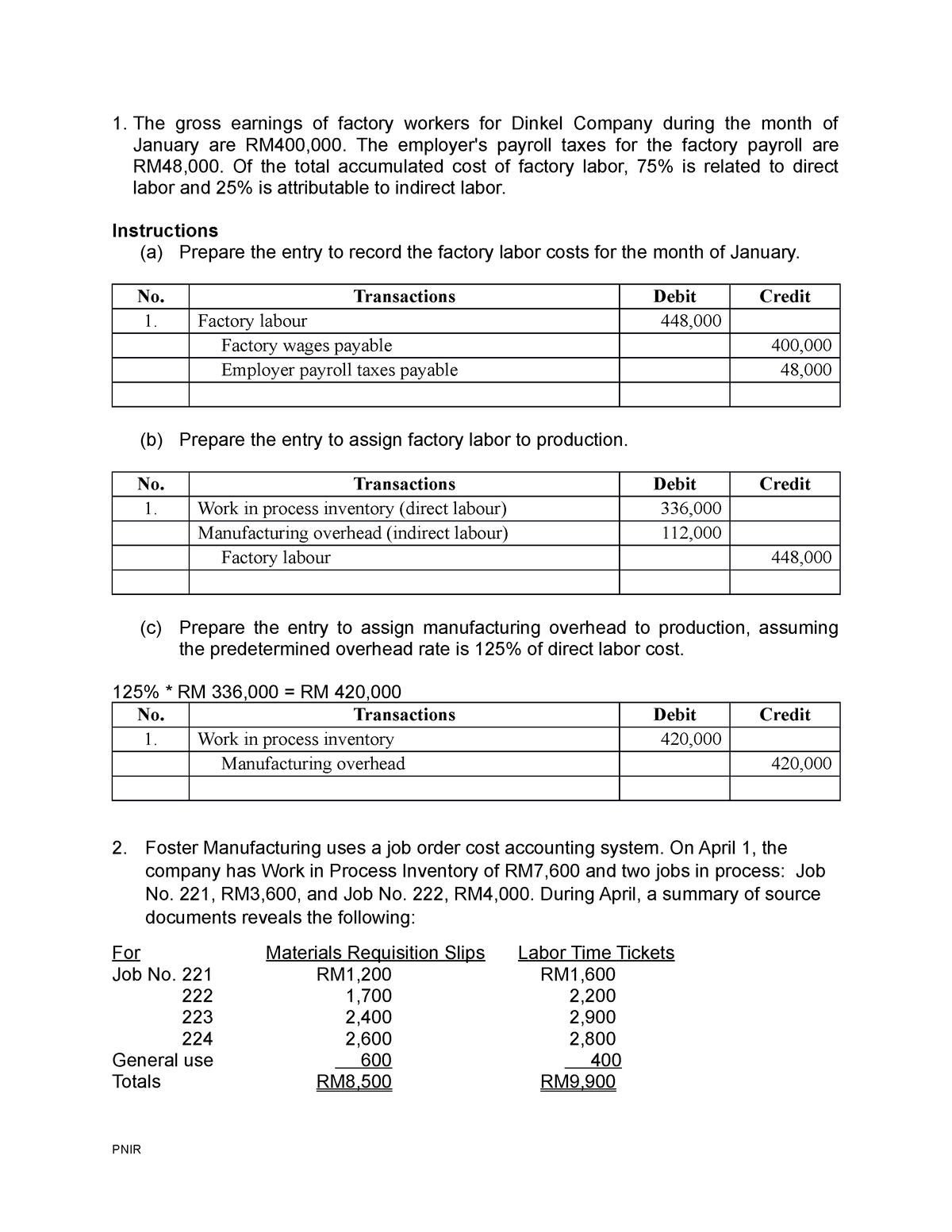
IS INDIRECT LABOR OVERHEAD?
If the actual overhead exceeds the applied overhead, they may wish to learn why the actual overhead is so high. Also, they may ask the accountants to increase the overhead applied to jobs to give them a better idea of the cost of jobs. If the actual is less than the applied overhead, they may ask the accountants to reduce the overhead applied to jobs.
Labor Cost Journal Entry
- Keeping a tab on the direct and indirect labor costs will help you exercise a strict control over labor cost and identify potential areas for cost improvement.
- We will discuss the difference between actual and applied overhead and how we handle the differences in the next sections.
- At the beginning of the year, the company used a cost formula to estimate that it would incur $\$ 4,800,000$ in manufacturing overhead cost at an activity level of 240,000 machine-hours.
- As a small business owner, it’s important to set the prices of your services and product high enough to cover your production costs, turn a profit, and still remain competitive.
- Ethics and the Manager LO3-4Terri Ronsin had recently been transferred to the Home Security Systems Division of National Home Products.
For example, the company ABC, which is a manufacturing company, has incurred the direct labor cost of $45,000 and the indirect labor cost of $5,000 during the period. Of the total amount, $42,000 is related to the wages payable and the $8,000 is related to the payroll taxes payable. Notice, Job 105 has been moved from FinishedGoods Inventory since it was sold and is now reported as an expensecalled Cost of Goods Sold. Also, did you notice that actualoverhead came to $9,800 ($1,000 indirect materials + $2,000indirect labor + $6,800 other overhead from transaction g) but weapplied $9,850 in overhead to the jobs in transaction d? Wheneverwe use an estimate instead of actual numbers, it should be expectedthat an adjustment is needed. We will discuss the differencebetween actual and applied overhead and how we handle thedifferences in the next sections.
Since this is an asset to asset transfer, we don’t make any changes to liabilities. Inventory is not just raw materials purchased and resold at a higher price. Instead, raw materials that the company purchases are “reworked” by employees before becoming sales, which allows them to be sold at a higher value.
And the payroll taxes payable account is a current liability account that the company owes to the applicable governing authorities. As a small business owner, it’s important to set the prices of your services and product high enough to cover your production costs, turn a profit, and still remain competitive. Keeping a tab on the direct and indirect labor costs will help you exercise a strict control over labor cost and identify potential areas for cost improvement. Underapplied and Overapplied Overhead LO3-4Osborn Manufacturing uses a predetermined overhead rate of $\$ 18.20$ per direct labor-hour.
If the applied overhead exceeds the actual amount incurred, overhead is said to be overapplied. This is usually viewed as a favorable outcome, because less has been spent than anticipated for the level of achieved production. Sometimes, in very specific cases, companies can do the same with salaries and wages. Just know that when they do, this is the final way labor can appear on the balance sheet — as a capitalized expense. When production of the group exceedsthe standard – 200 pieces per hour – each employee in the group ispaid a bonus for the excess production in addition to wages at hourlyrates. A company operates a piecework system of remuneration, but alsoguarantees its employees 75% of a time-based rate of pay which is basedon $19 per hour for an eight hour working day.
Assume Creative Printers is a company run by agroup of students who use desktop publishing to produce specialtybooks and instruction manuals. Creative Printers uses job costing.Creative Printers keeps track of the time and materials (mostlypaper) used on each job. Unless overtime is worked at the specific request of a customer, overtime premium is part of the indirect labour costs of an organisation. Vienna is a direct labour employee who works a standard 35 hoursper week and is paid a basic rate of $12 per hour. The remaining hours are the total hours spent by one employee as indirect labor utilization. Since indirect labor cannot be traced back to a specific product or service, the related cost can’t be billed to the goods produced or the services rendered.
Amounts go into the account and are then transferred out to other accounts. At this point, we need to credit (decrease) inventory for every sale we make. This increases cash or accounts payable not only by the value of the inventory, but also by the margin we make on it. Now we have both raw materials and wages in our WIP account, which we then need to transfer to the inventory account as products are completed.
The journal entry to apply or assign overhead to the jobs would be to move the cost FROM overhead TO work in process inventory. Although you have seen the job order costing system using both T-accounts and job cost sheets, it is necessary to understand how these transactions are recorded in the company’s general ledger. In job order costing, the direct labor will be transferred to the working in progress account while the indirect labor will be transferred to the manufacturing overhead account. In the accounting of job order costing, the labor cost account is usually used for recording the labor cost that incurs during the period including both direct labor and indirect labor.
The company can make the labor cost journal entry by debiting the labor cost account and crediting wages payable account and payroll taxes payable. In other words, employees’ salaries are a labor cost that must be considered as part of the raw materials’ transformation. More specifically, these labor costs are included as part of the inventory asset on the balance sheet in an account called Works in Progress (WIP). Here is a video discussion of job cost journal entries and then we will do an example. For example, Job 105 had revenue of USD 9,000 and costs of USD 5,500.Third, managers would compare actual overhead on the left side of the Overhead account, with the overhead applied to jobs on the right side.






